Dies ist eine alte Version des Dokuments!
GridBagLayout
Again and again you hear that the GridBagLayout is so complicated. It is really very extensive, but as a general rule you only need a few methods.
The GridBagLayout works fundamentally with a thought grid. Each array in this grid can be addressed by its position (x,y).
To define the size of the grid, you can outline the desired layout on a piece of paper.
With the class GridBagConstraints, the qualities of a single element are determined.
Example
The desired dialogue:
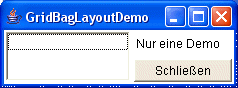
The beyond lying grid:
| 0,0 | 1,0 |
| 0,1 | 1,1 |
The list on the left side situated the two grid arrays 0,0 and 0,1.
Therefore, the height of the list is „2“. To assign a control (here of the list) to details of position and height, the class GridBagConstraints is used.
The go with it source looks like this:
package com.sowas.javademo.awt; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; public class GridBagLayoutDemo extends Frame implements ActionListener { Button btClose; public GridBagLayoutDemo(){ super("GridBagLayoutDemo"); GridBagLayout gbl=new GridBagLayout(); setLayout(gbl); GridBagConstraints gbc=new GridBagConstraints(); // Determine, that the GUI-elements fill out // the grid arrays in horizontal direction: gbc.fill=GridBagConstraints.HORIZONTAL; // Determine the distances of the single // GUI-elements to the thought grid lines: gbc.insets = new Insets(2,2,2,2); gbc.gridx = 0; // x-position in the thought grid gbc.gridy = 0; // y-position in the thought grid gbc.gridheight = 2; // two grid-arrays high List list = new List(3); gbl.setConstraints(list, gbc); add(list); gbc.gridx=1; gbc.gridy=0; gbc.gridheight = 1; Label label = new Label("Only a demo"); gbl.setConstraints(label, gbc); add(label); gbc.gridx=1; gbc.gridy=1; gbc.gridheight = 1; btClose = new Button("close"); btClose.addActionListener(this); gbl.setConstraints(btClose, gbc); add(btClose); pack(); } public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e){ if (e.getSource() == btClose) dispose(); } public static void main(String[] args){ GridBagLayoutDemo demo = new GridBagLayoutDemo(); demo.setVisible(true); } }
Natürlich hat das GridBagLayout noch mehr Möglichkeiten. Häufig verwendet werden auch noch die GridBagConstraints-Parameter
weightx
und
weighty
. Diese können Werte zwischen 0.0 und 1.0 einnehmen und geben an, wie der verbleibende Freiraum aufgeteilt wird. Beispiel: Ein Dialog habe eine verfügbare Breite von 600 Pixeln. In diesem Dialog seien zwei Elemente A und B angeordnet. Dabei habe Element A ein minimalen Platzbedarf von 300 Pixeln und Element B einen minimalen Platzbedarf von 100 Pixeln. Damit bleiben 200 Pixel über. Diese werden im Verhältnis der beiden Werte für weightx aufgeteilt. Angenommen Element A habe ein weightx von 0.75 und Element B ein weigtx von 0.25, so wird das Gitterfeld für A eine Breite von 450 Pixeln (300+0.75*200) und Gitterfeld B eine Breite von 150 (100+0.25*200) Pixeln erhalten.
Wird ergänzt…